Energy Audits: Energy & Environment Management
Context
Regarding the political, social and environmental context in which we live today, we can assure that energy is precious good which optimization and usage must be optimized. Therefore, it is important to make a good energy management, what often passes for conducting energy audits.
In addition to a good energy management to protect the environment, an energy audit also provides a greater knowledge of the facilities, reducing or even aborting, in some cases, avoidable consumption during the operation.
The Benefits
Having said that, it is possible to enumerate some of the following benefits of conducting energy audits of its facilities:
- Increased energy efficiency of installed equipment;
- Reducing the energy bill;
- Increase the productivity of the enterprise;
- Better knowledge of the facilities and the energy cost of each stage of the process;
- Reduction of the unit cost of production;
- Identify situations of energy waste and fix them;
- Reduction of environmental impact;
- Access to financial assistance in energy investments.
Energy audits provide information and identify real opportunities to save energy, as a study of how energy is used.
Phases of the Process
This examination is carried out correctly, there is some information that is needed and required by the Auditors:
- Description of the activity;
- Main production processes;
- Types of energy;
- Types of consumption;
- Main consumers of energy (equipment);
- Verification of the existence of responsible for energy management;
- Diagnosis of energy audits performed in the past;
- The facilities to be audited.
The methodology used in performing an energy audit consists of four phases of intervention:
Phase 1: Audit and Visit to the Installations
In this phase it is fundamental to the preparation of the audit and the visit to the installations, being decisive for the success. This first phase is usually composed of the following tasks:
- Prior visit to the installations;
- Collecting the data corresponding to the historical records of the last three years of activity;
- Study and analysis of the productive process implemented on the premises to audit;
- Survey of process technologies and energy technologies available on the market, characterized by a high efficiency;
- The prior visit allows a first contact with the installation, it must be made at this phase a profound analysis of the implemented process, establishing the processes flowcharts which must go along with the auditors in the field work, developed later.
On the second phase, are made a set of measurements, if applicable, for posterior report elaboration:
- Energy consumption measurements on the installation;
- Flow and enthalpy measurement of fluids;
- Thermographic analysis;
- Analysis of the electrical network;
- Combustion efficiency analysis;
- Analysis of efficiency and determination of specific consumption of equipment and systems.
With the report concluded, follows the phase of data collection analysis for the posterior implementation of the actions that better fit to each case and that allows real savings that were being spent unnecessarily, representing a cost to the company and for the environment.
At this phase the following data are analyzed:
- Rationalization plans for energy consumption;
- Process energy optimization;
- Technical and economic feasibility studies;
- Financial analysis of energy rationing solutions.
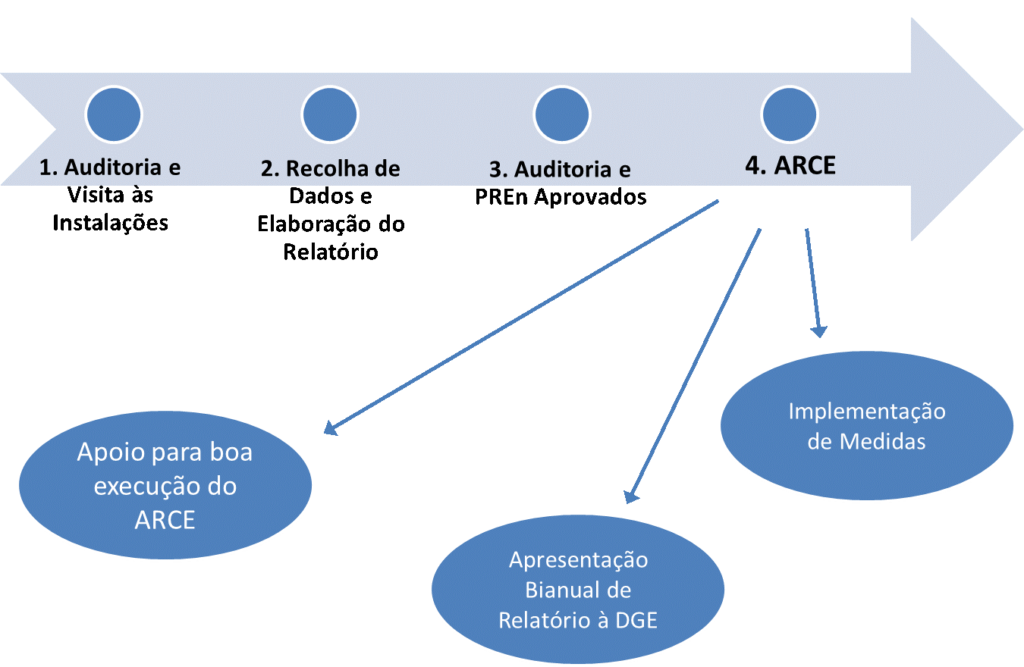
Phase 4: ARCE
At this last phase of the process, the following occurs:
- Implementation of the energy management plan;
- Implementation of solutions to reduce energy consumption;
- Follow-up of the rationalization plan for energy consumption.
In this phase, the correct implementation of the improvement actions is fundamental, so that the energy savings are really noticed and the audited capital gains are verified, as described at the beginning of this article.
TecnoVeritas’ Role
TecnoVeritas, with more than 20 years in the market, has a specialized team, not only in energy audits but also in the implementation of standards, such as ISO 50001, dedicated to energy management.